Spring
Quick intro
What is Spring?
Spring Framework or Spring Boot?
Spring Framework
The Spring Framework provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for modern Java-based enterprise applications - on any kind of deployment platform.
A key element of Spring is infrastructural support at the application level: Spring focuses on the "plumbing" of enterprise applications so that teams can focus on application-level business logic, without unnecessary ties to specific deployment environments.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run".
We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need minimal Spring configuration.
Inversion of Control
In software engineering, inversion of control (IoC) is a programming principle. IoC inverts the flow of control as compared to traditional control flow.
A software architecture with this design inverts control as compared to traditional procedural programming: in traditional programming, the custom code that expresses the purpose of the program calls into reusable libraries to take care of generic tasks, but with inversion of control, it is the framework that calls into the custom, or task-specific, code.
What?...
Simpler Version
Inversion of Control (IoC) means to create instances of dependencies first and latter instance of a class, instead of creating an instance of the class first and then the class instance creating instances of dependencies
Dependency Injection
In software engineering, dependency injection is a design pattern in which an object or function receives other objects or functions that it depends on. A form of inversion of control, dependency injection aims to separate the concerns of constructing objects and using them, leading to loosely coupled programs3 ways of injecting:
- Constructor injection, where dependencies are provided through a client's class constructor.
- Setter injection, where the client exposes a setter method which accepts the dependency.
- Interface injection, where the dependency's interface provides an injector method that will inject the dependency into any client passed to it.
Simplest Vanilla Example
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Build the service
Service service = new ExampleService();
// Inject the service into the client
Client client = new Client(service);
// Use the objects
System.out.println(client.greet());
}
}
Dependency Injection in Spring
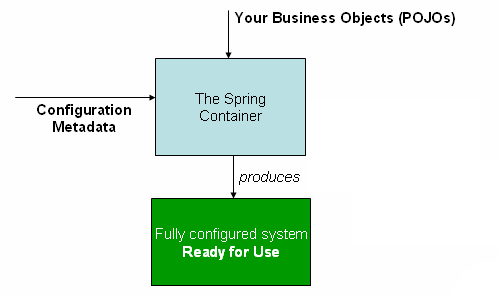
ApplicationContext
Ways to define a Bean
- Annotation-based configuration
- Java-based configuration
No XML here
Stereotype annotations
- @Component
- @Service
- @Repository
- @Controller
- @Indexed
Define a bean with a stereotype annotation
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Rocket {}
Configuration class
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
public class Rocket {}
@Configuration
public class RocketConfiguration {
@Bean
public Rocket superDuperRocket() {
return new Rocket();
}
}
@ComponentScan
Configures component scanning directives for use with @Configuration classes
Either basePackageClasses() or basePackages() (or its alias value()) may be specified to define specific packages to scan. If specific packages are not defined, scanning will occur from the package of the class that declares this annotation.

How to inject a bean?
- @Resource
- @Inject
- @Autowired
Injecting bean - where do we do that?
- Constructor based injection
- Setter based injection
- Field based injection
Injecting a bean - constructor
@Component
public class Rocket {}
@Service
public class SpaceFlight {
private Rocket rocket;
@Autowired
public SpaceFlight(Rocket rocket) {
this.rocket = rocket;
}
}
Injecting a bean - setter
@Component
public class Rocket {}
@Service
public class SpaceFlight {
private Rocket rocket;
@Autowired
public void setRocket(Rocket rocket) {
this.rocket = rocket;
}
}
Injecting a bean - field
@Component
public class Rocket {}
@Service
public class SpaceFlight {
@Autowired
private Rocket rocket;
}
Quiz time!
@Component
public class Rocket {}
@Service
public class SpaceFlight {
private Rocket rocket;
public SpaceFlight(Rocket rocket) {
this.rocket = rocket;
}
}
Quiz time!
@Component
public class Foo {
private final Bar bar;
public Foo(Bar bar) {
this.bar = bar;
}
}
@Component
public class Bar {
private final Foo foo;
public Bar(Foo foo) {
this.foo = foo;
}
}
Quiz time!
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
The dependencies of some of the beans
in the application context form a cycle:
┌─────┐
| bar defined in file [.../Bar.class]
↑ ↓
| foo defined in file [.../Foo.class]
└─────┘
Action:
Relying upon circular references is discouraged and
they are prohibited by default.
Update your application to remove the
dependency cycle between beans.
As a last resort, it may be possible
to break the cycle automatically by setting
spring.main.allow-circular-references to true.
Let's try to force that
In application.yml we add:
spring.main.allow-circular-references: true
and we get...
Action:
Despite circular references being allowed,
the dependency cycle between beans
could not be broken.
Update your application
to remove the dependency cycle.
This is how we hack Spring
@Component
public class Foo {
private Bar bar;
@Autowired
public void setBar(Bar bar) {
this.bar = bar;
}
}
@Component
public class Bar {
private Foo foo;
@Autowired
public void setFoo(Foo foo) {
this.foo = foo;
}
}
More questions...
public interface Rocket {
String getRocketCallSign();
}
@Service
public class NasaRocket implements Rocket{
@Override
public String getRocketCallSign() {
return "Saturn V";
}
}
@Service
public class SpaceXRocket implements Rocket {
@Override
public String getRocketCallSign() {
return "Falcon 9";
}
}
@Service
public class RocketLauncher {
private Rocket rocket;
public RocketLauncher(Rocket rocket) {
this.rocket = rocket;
}
}
Description:
Parameter 0 of constructor in RocketLauncher
required a single bean, but 2 were found:
- nasaRocket: defined in file [.../NasaRocket.class]
- spaceXRocket: defined in file [.../SpaceXRocket.class]
Action:
Consider marking one of the beans as @Primary,
updating the consumer to accept multiple beans,
or using @Qualifier to identify
the bean that should be consumed
Primary
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
@Primary
@Service
public class NasaRocket implements Rocket{
@Override
public String getRocketCallSign() {
return "Saturn V";
}
}
Qualifier
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
@Service
public class RocketLauncher {
private Rocket rocket;
public RocketLauncher
(@Qualifier(value = "spaceXRocket") Rocket rocket) {
this.rocket = rocket;
}
}
Multiple beans of the same type
@Service
public class RocketLauncher {
private List<Rocket> rockets;
public RocketLauncher(List<Rocket> rockets) {
this.rockets = rockets;
}
void fireRockets() {
rockets.stream()
.map(Rocket::getRocketCallSign)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}No more
Time to get our hands dirty!
Create a simple app
- Project: Gradle Project
- Language: Java
- Version: 2.7.2 (Stable)
- Packaging: Jar
- Java Version: 11 / 17
Dependencies
Operations within that controller
- Get single rocket
- Get all rockets
- Create a rocket
- Delete a rocket
Rocket in a database
@Entity
public class Rocket {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(name = "callsign", nullable = false)
private String callSign;
// Important
public Rocket() {
}
public Rocket(String callSign) {
this.callSign = callSign;
}
// Getters and setters
}@Entity
An entity is a lightweight persistence domain object. Typically, an entity represents a table in a relational database, and each entity instance corresponds to a row in that table. The primary programming artifact of an entity is the entity class, although entities can use helper classes.
Requirements
- The class must be annotated with the javax.persistence.Entity annotation.
- The class must have a public or protected, no-argument constructor. The class may have other constructors.
- The class must not be declared final. No methods or persistent instance variables must be declared final.
- and more...
@Id
Specifies the primary key of an entity. The field or property to which the Id annotation is applied should be one of the following types: any Java primitive type; any primitive wrapper type; String; java.util.Date; java.sql.Date; java.math.BigDecimal; java.math.BigInteger.
@GeneratedValue
Provides for the specification of generation strategies for the values of primary keys. The GeneratedValue annotation may be applied to a primary key property or field of an entity or mapped superclass in conjunction with the Id annotation. The use of the GeneratedValue annotation is only required to be supported for simple primary keys. Use of the GeneratedValue annotation is not supported for derived primary keys.
@Column
Specifies the mapped column for a persistent property or field. If no Column annotation is specified, the default values apply.
Rocket in a database
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface RocketsRepository
extends JpaRepository<Rocket, Long> {}
Rocket in transport
public class RocketDto {
private long id;
private String callsign;
public RocketDto(long id, String callsign) {
this.id = id;
this.callsign = callsign;
}
public static RocketDto from(Rocket rocket) {
return new RocketDto(rocket.getId(), rocket.getCallSign());
}
// Getters and setters
Rocket in transport
public class CreateRocketDto {
private String callsign;
@JsonCreator
public CreateRocketDto(@JsonProperty("callsign") String callsign) {
this.callsign = callsign;
}
public String getCallsign() {
return callsign;
}
public void setCallsign(String callsign) {
this.callsign = callsign;
}
}
Use the rockets!
@Service
public class RocketService {
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
// ???
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
/// ???
}
public RocketDto createRocket(CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
/// ???
}
public boolean deleteRocket(Long rocketId) {
/// ???
}
}
We need the data
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
}
Get single rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
// ???
}
}
Get single rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
}
Get all rockets
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
// ???
}
}
Get all rockets
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
return rocketsRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(RocketDto::from)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
Create a rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
return rocketsRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(RocketDto::from)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public RocketDto createRocket(CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
// ???
}
}
Create a rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
return rocketsRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(RocketDto::from)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public RocketDto createRocket(CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
final Rocket rocket = new Rocket(createRocketDto.getCallsign());
return RocketDto.from(rocketsRepository.saveAndFlush(rocket));
}
}
Delete a rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
return rocketsRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(RocketDto::from)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public RocketDto createRocket(CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
final Rocket rocket = new Rocket(createRocketDto.getCallsign());
return RocketDto.from(rocketsRepository.saveAndFlush));
}
public boolean deleteRocket(Long rocketId) {
// ???
}
}
Delete a rocket
@Service
public class RocketService {
private final RocketsRepository rocketsRepository;
public RocketService(RocketsRepository rocketsRepository) {
this.rocketsRepository = rocketsRepository;
}
public Optional<RocketDto> getRocket(Long rocketId) {
return rocketsRepository.findById(rocketId)
.map(RocketDto::from);
}
public List<RocketDto> getAllRockets() {
return rocketsRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(RocketDto::from)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public RocketDto createRocket(CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
final Rocket rocket = new Rocket(createRocketDto.getCallsign());
return RocketDto.from(rocketsRepository.saveAndFlush));
}
public boolean deleteRocket(Long rocketId) {
if (rocketsRepository.existsById(rocketId)) {
rocketsRepository.deleteById(rocketId);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
@RestController
A convenience annotation that is itself annotated with @Controller and @ResponseBody.
Types that carry this annotation are treated as controllers where @RequestMapping methods assume @ResponseBody semantics by default.
@ResponseBody - Annotation that indicates a method return value should be bound to the web response body. Supported for annotated handler methods.
@RequestMapping
Annotation for mapping web requests onto methods in request-handling classes with flexible method signatures.
This annotation can be used both at the class and at the method level. In most cases, at the method level applications will prefer to use one of the HTTP method specific variants @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping, or @PatchMapping.
Let's write a controller
Define a REST controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
Add the service
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
private final RocketService rocketService;
public RocketController(RocketService rocketService) {
this.rocketService = rocketService;
}
Get all rockets
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@GetMapping
public List<RocketDto> getRockets() {
// ???
}
Get all rockets
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@GetMapping
public List<RocketDto> getRockets() {
return rocketService.getAllRockets();
}
Get single rocket
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@GetMapping("/{rocketId}")
public ResponseEntity<RocketDto> getRocket(
@PathVariable("rocketId") Long rocketId) {
// ???
}
@PathVariable
Annotation which indicates that a method parameter should be bound to a URI template variable. Supported for RequestMapping annotated handler methods. If the method parameter is Map<String, String> then the map is populated with all path variable names and values.
Get single rocket
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@GetMapping("/{rocketId}")
public ResponseEntity<RocketDto> getRocket(
@PathVariable("rocketId") Long rocketId) {
return rocketService.getRocket(rocketId)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElse(ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
ResponseEntity
Extension of HttpEntity that adds an HttpStatus status code. Used in RestTemplate as well as in @Controller methods.
@ResponseStatus
Marks a method or exception class with the status code() and reason() that should be returned. The status code is applied to the HTTP response when the handler method is invoked and overrides status information set by other means, like ResponseEntity or "redirect:".
Create a rocket
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@PostMapping
public RocketDto createRocket(@RequestBody CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
// ???
}
@RequestBody
Annotation indicating a method parameter should be bound to the body of the web request. The body of the request is passed through an HttpMessageConverter to resolve the method argument depending on the content type of the request. Optionally, automatic validation can be applied by annotating the argument with @Valid.
Create a rocket
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1/rockets")
public class RocketController {
@PostMapping
public RocketDto createRocket(@RequestBody CreateRocketDto createRocketDto) {
return rocketService.createRocket(createRocketDto);
}
Try it out!
curl localhost:8080/v1/rockets -v
curl -X POST localhost:8080/v1/rockets
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-d '{"callsign":"Falcon Heavy"}'
curl localhost:8080/v1/rockets/1 -v
curl -X DELETE localhost:8080/v1/rockets/1 -v